OTOPLASTY, PROTRUDING EAR SURGERY
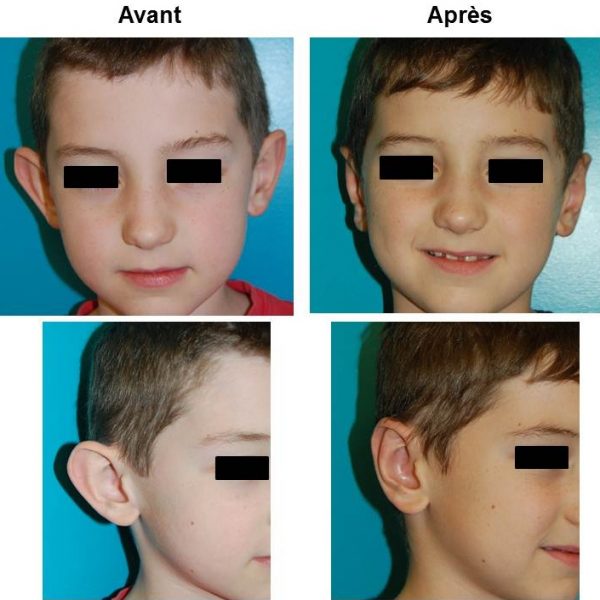
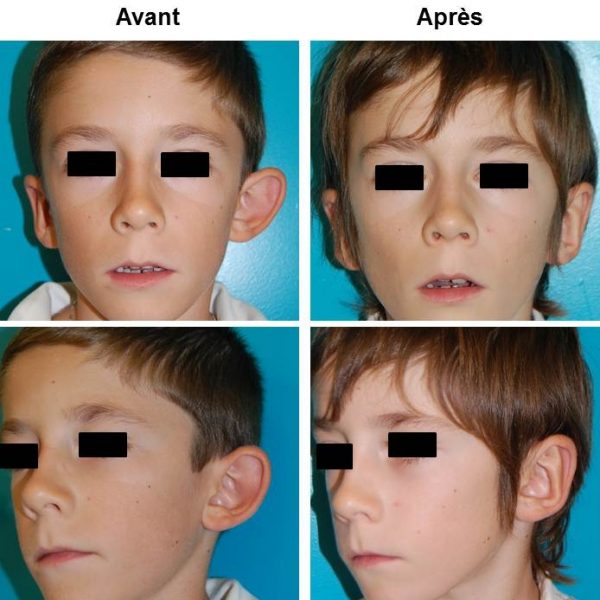
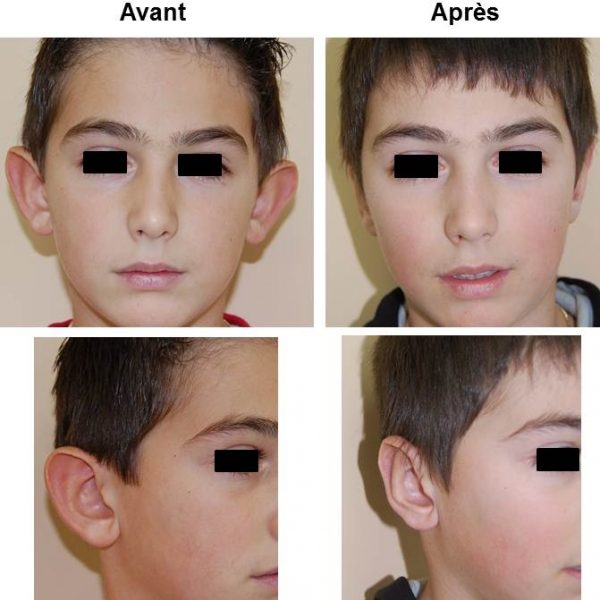
Otoplasty is a surgerical act which consists in repositioning and reshaping the ears presenting malformations (excessive angulation, cartilage defect cartilage or central cartilage hypertrophy). Usually, both ears are prominent but sometimes only one is concerned by the defect. The procedure can be done on children when the ear growth is correct, approximately 7 years old. Adults, however, may have surgery at any age.
> all about PROTRUDING EAR SURGERY (OTOPLASTY) <
COSMETIC SURGERY OF THE EARS (OTOPLASTY) IN MONTREUX, GENEVA AND LAUSANNE SWITZERLAND
Cosmetic surgery of prominent ears is also called otoplasty. Since both ears are usually detached the surgical procedure targets them equally. In rare occasions, only one ear is detached and has to be reattached separately.
This procedure of aesthetic surgery aims to correct cartilage defects of the external ear that gives this protruding appearance.
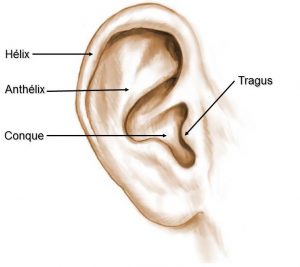
There are three categories of defects that are often associated with each other (Figure 1):
– An angle that is too large (too open) between the concha cava (bowl of the ear) and the skull, causing a detachment of the whole pinna: the concha bowl default.
– An excessive size of the concha cartilage causing a forward projection of the ear, which increases the protruding aspect of the ears is called the hypertrophy of the concha.
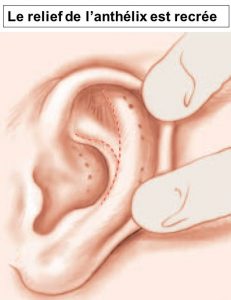
-A kinking default of the regular cartilage shape. Thus, the ear pavilion looks smooth and without reliefs: this is the anthelix plication default.
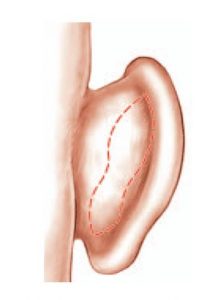
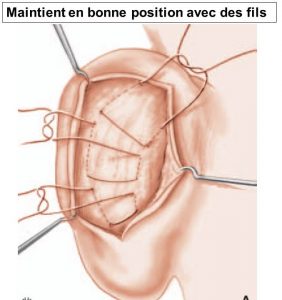
Otoplasty will correct these defects by reshaping and suturing the cartilage to place the ears closer to the skull, with a natural look. This intervention will stop mocking and disparaging criticisms that can cause psychological disorders and learning difficulties to children.
Cosmetic surgery of protruding ears can be done on both adults and adolescents. Most often otoplasty is planned and conducted on children from the age of 7. At this age the ears have finished growing and have reached their final height. It is fundamental to clarify that otoplasty cannot be achieved without the desire and motivation of the child.